What is the SQL Server equivalent to Access IIf() function? Access SQL IIf([ResultValue]>=1, [Result Value], Null) SQL Server CASE WHEN [Result Value]>=1 THEN [Result Value] ELSE NULL END
Fixes or workarounds for recent issues in Access
Access crashes and slow performance Error: “Automatic configuration of the current version of Microsoft Access has failed.” occurs when you try to start Microsoft Access after updating to Version 1802 [FIXED] ISSUE You may get the following error when start Access after updating to Monthly Channel Version 1802 (Build 9029.2167 or higher): “Automatic configuration of…
Hardware Recommendations For Running Access
Hardware matters. Invest in a faster PC and your Microsoft Access databases will run faster. Be alert for sellers packaging fast processors with minimal memory and a slow hard drive to keep prices low. Look at all aspects of the purchase when database speed is a priority. A faster hard drive is worth the investment…
Use properties instead of constant or magic numbers
A common programming mistake is to hard-code literals that corresponds to some property. That is particularly true with certain controls like tab controls & pages. The tab control exposes a Value property that indicates the current tab and the pages contains a PageIndex property that indicates its position in the tabs of the control. Thus,…
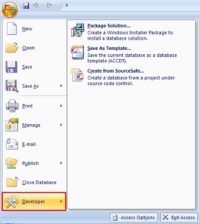
Access 2007: Access Developer Extensions
The Microsoft Office Access 2007 Developer Extensions make it easy to deploy and manage solutions built using Microsoft Access. The Access 2007 Developer Extensions provide packaging and deployment tools and licensing and distribution agreements to make it easier for developers to bring solutions to market. Whether you are working in a small business or a…
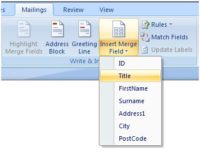
Using Microsoft Access Data in a Mail Merge
Suppose you have an Access Database containing the names and addresses of your customers. Every now and again you may want or need to send a standard letter to each customer who has opted in to such mailings. However, you are aware that these letters are going to look so much better, and work so…
Access InStr() function to SQL Server equivalent
What is the SQL Server equivalent to Access InStr() function? TargetField: String expression being searched SearchValue: String expression being sought StartPosition: Starting position for each search (optional) Access SQL InStr(TargetField, SearchValue) InStr(StartPosition, TargetField, SearchValue) SQL Server CHARINDEX(SearchValue, TargetField) CHARINDEX(SearchValue, TargetField, StartPosition)
Using Custom Functions in Calculated Controls
Custom functions work the same way as MS Access built-in functions such as DateAdd, DatePart and DSum, but are instead created ourselves as database developers. We do this by creating a public function with the VBA programming language and save it inside a global module within the database. Today I am going to explain how custom functions can be…