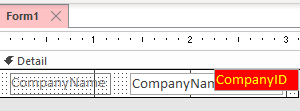
Sometimes we need to use fields from a RecordSource that aren’t shown on the form. It is legal to reference them directly even if they don’t have a control. For example, we can have a form bound to a RecordSource like so: SELECT c.CompanyID, c.CompanyName FROM Companies; And only display CompanyName in a textbox but…
Module level variables
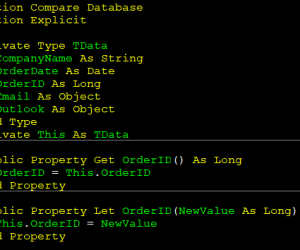
It is common to create a big wall of declaration in a module such as this: Private strCompanyName As String Private dteOrderDate As Date Private lngOrderID As Long Private objEmail As Object Private objOutlook As Object While the code will compile and work fine, the discoverability and naming of the module level variables does become…
Enable and Disable a Form Control using VBA
I was working on a design for an Order Management Database, and one of the tasks I dealt with involved dynamically Enabling or Disabling one of the form’s Command Buttons’ using VBA. This gave me the idea for the present Access tip. The command button was located on a Customer Details form which had an Orders…
Access IIf() function to SQL Server equivalent
What is the SQL Server equivalent to Access IIf() function? Access SQL IIf([ResultValue]>=1, [Result Value], Null) SQL Server CASE WHEN [Result Value]>=1 THEN [Result Value] ELSE NULL END
Prefer compile time errors over run time errors
In VBA, there are several features that allow us to do things that may not be checked at the compile time. In particular, it is possible to write several late-bound expressions which means that it can potentially contain run-time errors. One common misconception about late-binding is that it’s a matter of adding a reference and…
Normalize all constraints’ & indices’ names
Constraints that are created by SSMA or by user via SSMS tend to have ugly names. Worse, auto-generated names are not stable across backups. Meaning if you restore a new database based on a copy of another database, the constraint names will change. That create huge problems during migrations because scripts that references constraint will…
“Truthy” and “Falsy” Values
VBA is quite very loose in what it deems “truthy” and “falsy”. For example, this procedure can produce surprising result: If Me.MyBitField.Value = True Then ‘It is true Else ‘It is false End If At the first glance, it seems expected that if the bit field is set to 1, it would succeed. But in…
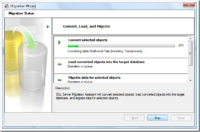
How to Migrate Data from Access to SQL Server using SSMA (SQL Server Migration Assistant)
SSMA is used to migrate Access databases to SQL Server. This tool converts the Access database to an SQL Server or an SQL Azure database. It is not bundled with SQL Server – you will need to download and install this tool separately. Check your system requirements and view the installation procedure for SSMA. Preparing…
Designing a lookup table with logic
It is very common for us to embed some kind of logic based on a lookup table or in some cases, a column of a table. Because we have application logic connected to it, the code are fragile and subject to changes as the requirements develops. We want to avoid this situation where we might…
“Too Few Parameters” error fix
Symptoms Whenever you run a SQL statement you get a “Too Few Parameters, expected X.” Cause Most common cause is misspelling or missing fields in the SQL statement. Resolution Check the SQL statement. If necessary, copy and paste to an Access query and test in the query to get it to highlight which part of…